Table of contents
- Setup an AWS EC2 Instance
- Install JDK on AWS EC2 Instance
- Install and Setup Jenkins
- Update visudo and assign administration privileges to jenkins user
- Install Docker
- Install and Setup AWS CLI
- Install and Setup Kubectl
- Install and Setup eksctl
- Creating an Amazon EKS cluster using eksctl
- Add Docker and GitHub Credentials on Jenkins
- Build, deploy and test CI/CD pipeline
- To set up Jenkins - GitHub Webhook
- Clean up
- Conclusion
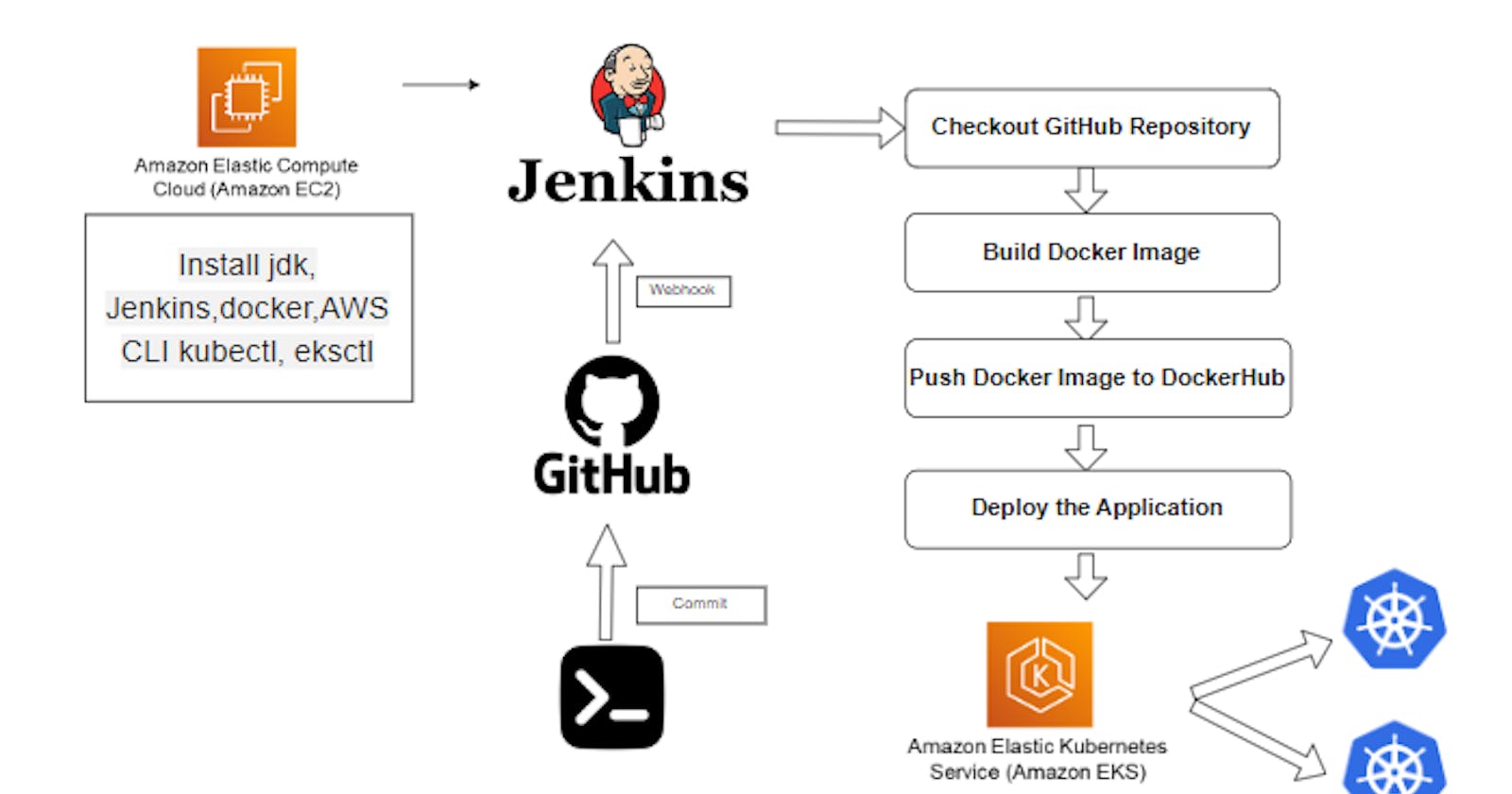
This article is about the deployment of the Node.js application on the Amazon EKS Kubernetes cluster. We will set up a pipeline with Jenkins.
Jenkins GitHub Webhook automates the build and deployment of applications when any commit is done to the source code.
Setup an AWS EC2 Instance
Login to an AWS account using a user with admin privileges and ensure your region is set to us-east-1 N. Virginia.
Move to the EC2 console. Click Launch Instance.
For name use Jenkins-EC2.

Select t2.medium because we will be installing Jenkins and t2.micro will not be sufficient enough to set up Jenkins.

Create and download the key pair(private key and public key)


Configure Security Group - This is an important step because here we need to add Custom TCP Port 8080, if you do not add this port then you will not be able to access Jenkins using the public IP address of the AWS EC2 instance.


Click on launch Instance and once EC2 Instance started, connect to it with EC2 Instance Connect.



Install JDK on AWS EC2 Instance
Before following the below steps, assume you have already launched the ubuntu-based ec2 medium instance.
Check if you have java already installed on your EC2 machine by running the following command -
sudo apt-get update
java --version

If this command indicates that Java is not found, then it’s not installed and you can proceed with the next steps.
You can install java by running the following command.
sudo apt install openjdk-11-jre-headless -y
java --version

Install and Setup Jenkins
Step 1: Install Jenkins
Follow the steps for installing Jenkins on the EC2 instance.
wget -q -O - https://pkg.jenkins.io/debian-stable/jenkins.io.key | sudo apt-key add -
sudo sh -c 'echo deb https://pkg.jenkins.io/debian-stable binary/ > /etc/apt/sources.list.d/jenkins.list'
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install jenkins
sudo systemctl status jenkins

Step 2: Setup Jenkins
Now go to AWS dashboard -> EC2 -> Instances(running)and click on Jenkins-EC2
Copy Public IPv4 address.
Alright now we know the public IP address of the EC2 machine, so now we can access Jenkins from the browser using the public IP address followed by port 8080.

If you are installing Jenkins for the first time then you need to supply the initialAdminPassword and you can obtain it from

After completing the installation of the suggested plugin you need to set the First Admin User for Jenkins.



And now your Jenkins is ready for use

Update visudo and assign administration privileges to jenkins user
Now we have installed the Jenkins on the EC2 instance. To interact with the Kubernetes cluster Jenkins will be executing the shell script with the Jenkins user, so the Jenkins user should have an administration(superuser) role assigned forehand.
Let's add jenkins user as an administrator and also ass NOPASSWD so that during the pipeline run it will not ask for root password.
Open the file /etc/sudoers in vi mode
sudo vi /etc/sudoers
Add the following line at the end of the file
jenkins ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD: ALL
After adding the line save and quit the file.
Now we can use Jenkins as root user and for that run the following command -
sudo su - jenkins
Install Docker
The docker installation will be done by the Jenkins user because now it has root user privileges.
Add jenkins user to Docker group. Jenkins will be accessing the Docker for building the application Docker images, so we need to add the Jenkins user to the docker group.
sudo apt install docker.io
docker --version
docker ps
sudo usermod -aG docker jenkins
sudo reboot

Install and Setup AWS CLI
Now we need to set up the AWS CLI on the EC2 machine so that we can use eksctl in the later stages
Let us get the installation done for AWS CLI 2
sudo apt install awscli
curl "https://awscli.amazonaws.com/awscli-exe-linux-x86_64.zip" -o "awscliv2.zip"
unzip awscliv2.zip
sudo ./aws/install --update
aws --version

Okay now after installing the AWS CLI, let's configure the AWS CLI so that it can authenticate and communicate with the AWS environment.
aws configure
To configure the AWS the first command we are going to run is
Once you execute the above command it will ask for the following information -
AWS Access Key ID [None]:
AWS Secret Access Key [None]:
Default region name [None]:
Default output format [None]:
You can click on the Create New Access Key and it will let you generate - AWS Access Key ID, AWS Secret Access Key.
(Note: - Always remember you can only download your access id and secret once, if you misplace the secret and access then you need to recreate the keys again.

Install and Setup Kubectl
Moving forward now we need to set up the kubectl also onto the EC2 instance where we set up the Jenkins in the previous steps.
Here is the command for installing kubectl
curl -LO "https://storage.googleapis.com/kubernetes-release/release/$(curl -s https://storage.googleapis.com/kubernetes-release/release/stable.txt)/bin/linux/amd64/kubectl"
chmod +x ./kubectl
sudo mv ./kubectl /usr/local/bin
kubectl version

Verify the kubectl installation by running the command kubectl version and you should see the following output.

Install and Setup eksctl
Okay, the first command which we are gonna run to install the eksctl
Download and extract the latest release of eksctl with the following command.
curl --silent --location "https://github.com/weaveworks/eksctl/releases/latest/download/eksctl_$(uname -s)_amd64.tar.gz" | tar xz -C /tmp
Move the extracted binary to /usr/local/bin.
sudo mv /tmp/eksctl /usr/local/bin
Test that your installation was successful with the following command.
eksctl version

Creating an Amazon EKS cluster using eksctl
Now in this step, we are going to create Amazon EKS cluster using eksctl
You need the following in order to run the eksctl command
Name of the cluster : --name first-eks-cluster1
Version of Kubernetes : --version 1.24
Region : --region us-east-1
Nodegroup name/worker nodes : --nodegroup-name worker-nodes
Node Type : --nodegroup-type t2.micro
Number of nodes: --nodes 2
Here is the eksctl command -
eksctl create cluster --name first-eks-cluster1 --version 1.24 --region us-east-1 --nodegroup-name worker-nodes --node-type t2.micro --nodes 2
It took me 20 minutes to complete this EKS cluster. If you get any error for not having sufficient data for mentioned availability zone then try it again.
Verify the EKS kubernetes cluster on AWS Console.
You can go back to your AWS dashboard and look for Elastic Kubernetes Service -> Clusters


Add Docker and GitHub Credentials on Jenkins
Step 1: Setup Docker Hub Secret Text in Jenkins
You can set the docker credentials by going into -
Goto -> Jenkins -> Manage Jenkins -> Manage Credentials -> Stored scoped to jenkins -> global -> Add Credentials

Step 2. Setup GitHub Username and password into Jenkins
Now we add one more username and password for GitHub.
Goto -> Jenkins -> Manage Jenkins -> Manage Credentials -> Stored scoped to jenkins -> global -> Add Credentials


Build, deploy and test CI/CD pipeline
Okay, now we can start writing out the Jenkins pipeline for deploying the Node.js Application into the Kubernetes Cluster.
Create new Pipeline: Goto Jenkins Dashboard or Jenkins home page click on New Item

Pipeline Name: Now enter Jenkins pipeline name and select Pipeline


Add pipeline script: Goto -> Configure and then pipeline section.

Copy the below script and paste into Pipeline Script.
node {
stage("Git Clone"){
git credentialsId: 'GIT_HUB_CREDENTIALS', url: 'https://github.com/sunitabachhav2007/node-todo-cicd.git', branch: 'master'
}
stage("Build") {
sh 'docker build . -t sunitabachhav2007/node-todo-test:latest'
sh 'docker image list'
}
withCredentials([string(credentialsId: 'DOCKER_HUB_PASSWORD', variable: 'PASSWORD')]) {
sh 'docker login -u sunitabachhav2007 -p $PASSWORD'
}
stage("Push Image to Docker Hub"){
sh 'docker push sunitabachhav2007/node-todo-test:latest'
}
stage("kubernetes deployment"){
sh 'kubectl apply -f deployment.yml'
}
}
To set up Jenkins - GitHub Webhook
Now, go to the “Build Triggers” tab.
Here, choose the “GitHub hook trigger for GITScm pulling” option, which will listen for triggers from the given GitHub repository, as shown in the image below.

Jenkins GitHub Webhook is used to trigger the action whenever Developers commit something into the repository. It can automatically build and deploy applications.
Switch to your GitHub account, go to “Settings” option. Here, select the “Webhooks” option and then click on the “Add Webhook”
It will provide you the blank fields to add the Payload URL where you will paste your Jenkins address, Content type, and other configuration.
Go to your Jenkins tab and copy the URL then paste it in the text field named “Payload URL“, as shown in the image below. Append the “/github-webhook/” at the end of the URL.


You completed Jenkins GitHub Webhook. Now for any commit in the GitHub repository, Jenkins will trigger the event specified



After pushing code to Github repository


You can access the rest endpoint from a browser using the EXTERNAL-IP address.

Clean up
Copy Deployment.yml file (From Github Repository) to EC2 server and run with below command.
kubectl delete -f deployment.yml
Delete EKS Cluster from AWS Console.

Terminate EC2 Instance.

Conclusion
We have successfully deployed our Node.js App in Amazon EKS cluster using AWS EC2, Jenkins, Docker, Kubernetes, GitHub, Webhook.
If you have liked this project and my effort please share this and fork my Github repo for more practice.
.